Article Text
Abstract
Background/aims Cortisol is involved in the regulation of intraocular pressure (IOP). This study aimed to assess the effect of 11β-hydroxysteroid-dehydrogenase type 1 (11βHSD1) inhibition by oral administration of RO5093151 on IOP.
Methods The exposure of key ocular compartments following oral administration was assessed in rabbits. An adaptive, randomised, placebo-controlled study gated by a Bayesian decision criterion was performed in 35 patients with primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) or ocular hypertension (OHT). Following a 7-day placebo-controlled run-in period, 200 mg twice daily RO5093151 or placebo (4:1) were administered for 7 days. The extent of 11βHSD1 inhibition was assessed by the ratio of urinary tetrahydrocortisol (5α and 5β)/tetrahydrocortisone (THF/THE). Time-matched IOP assessments were performed.
Results A high distribution of RO5093151 into the rabbit eye was observed. In humans, a high and sustained inhibition of 11βHSD1 was shown by the decrease of THF/THE from 0.9 at baseline to 0.18 on day 7. There was no statistically significant difference in change of IOP from baseline. In the ‘worse eye’, the adjusted least square mean change from baseline was −2.7 mm Hg (95% CI −4.2 to –1.2) and −2.9(95% CI −5.9 to 0.1) in the RO5093151 and placebo group, respectively.
Conclusions Despite high inhibition of 11βHSD1 and expected moderate to high tissue distribution in ocular tissues, a 7-day treatment with a high oral dose of RO5093151 did not result in a clinically meaningful effect on IOP in patients with POAG or OHT.
- IOP
- 11β-HSD
- clinical trial
- glaucoma
This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Key messages
Ocular inhibition of 11β-hydroxysteroid-dehydrogenase (11βHSD) has been suggested in the literature to decrease intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) or ocular hypertension (OHT).
We did not find a clinically relevant IOP reduction of the highly selective and potent 11β-hydroxysteroid-dehydrogenase type 1 (11βHSD1) inhibitor RO5093151 in patients with POAG and OHT following oral administration.
The clinical trial design included a placebo-controlled run-in period for all patients and a Bayesian decision criterion to test for success based on an absolute 5 mm Hg IOP reduction. This allowed for a relatively small sample size to conclude on lack of efficacy.
High ocular RO5093151 concentrations in the rabbit following oral administration, together with the clinical observation of high unbound drug concentrations well above the IC50 value of 11βHSD1 inhibition and high systemic 11βHSD1 inhibition suggested sufficiently high ocular concentrations of RO5093151 were achieved.
Inhibition of 11βHSD1 is not a promising target to reduce IOP in patients with POAG or OHT. Further studies are required to investigate the benefit of 11βHSD1 inhibition in patients with steroid-induced glaucoma.
Introduction
Elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) is a key risk factor in the development and progression of vision impairment in glaucoma with over 60 million affected individuals worldwide.1 Ocular hypotensive therapy remains the mainstay in the pharmacological treatment for primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) and ocular hypertension (OHT).2 3 The pharmacological interventions currently available mainly target the turnover of the aqueous humour by either reducing the production or increasing its outflow.2
The use of topical and systemic glucocorticoids can result in corticosteroid-induced glaucoma. This condition is associated with an increase in IOP, which ultimately can lead to visual field loss and blindness. Several lines of evidence implicate the involvement of cortisol in the regulation of IOP: (A) an analysis of diurnal IOP curves found in 40% of cases the highest IOP at the earliest morning measurement with 65% of the peaks occurring before noon,4 (B) raised IOP can also occur in patients with Cushing’s syndrome5 and (C) an increase in plasma cortisol levels has been reported in patients with OHT and POAG,4 indicative of an alteration of the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal axis in these patients.
Glucocorticoids are proposed to have effects both on aqueous humour production in non-pigmented epithelial cells of the ciliary body6–9 and on reducing outflow through the trabecular meshwork by changing its morphology.10 Cortisol levels in the eye are not merely a reflection of circulating cortisol levels but are actively controlled by the two enzymes 11β-hydroxysteroid-dehydrogenase type 1 (11βHSD1) and 11β-hydroxysteroid-dehydrogenase type 2 (11βHSD2), the former transforming cortisone into the active form cortisol, the latter facilitating the reverse. 11βHSD1 was shown to be expressed in human basal cells of the corneal epithelium and in a ciliary non-pigmented epithelial cell-line, while 11βHSD2 was restricted to the corneal endothelium.9 Therefore, increased IOP was hypothesised to be linked to increased ocular cortisol levels, which could be reduced by inhibition of 11βHSD1.11
RO5093151 is a potent and highly selective inhibitor of human 11βHSD1, which showed to decrease the urinary cortisol/cortisone metabolite ratio of tetrahydrocortisol (5α and 5β)/tetrahydrocortisone (THF/THE) as surrogate of total body 11βHSD1 inhibition.12 13 Overall, RO5093151 was shown to have a good safety profile in clinical studies using doses of up to 200 mg twice daily for up to 12 weeks.
Glaucoma medications are typically administered by topical administration. Based on the available evidence of the role of 11βHSD1 in IOP regulation provided above, a preclinical study was first conducted to assess the ocular exposure of RO5093151 after oral administration, followed by a clinical study testing the effect of orally administered RO5093151 on IOP in patients with OHT or POAG.
Methods
Exploratory study to assess ocular exposure of RO5093151 in the rabbit
The animal experiments were conducted at Iris Pharma, La Gaude, France, in 2011. All animals were treated according to the European Convention (French Decree N° 2001–486, dated 6 June 2001) and to the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Statement for the Use of Animals in Ophthalmic and Vision Research (Handbook for the Use of Animals in Biomedical Research second ed., 1993).
A single oral dose of 30 mg/kg RO5093151 was administered to 12 pigmented rabbits. At 0.5, 2, 6 and 12 hours post-dose, three rabbits at each time-point were sacrificed and samples from plasma, tears, cornea, ciliary body and aqueous humour were analysed for RO5093151 using a non-validated liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS)/MS method. Ocular tissues were collected for both eyes.
Clinical efficacy, safety and tolerability of RO5093151 in patients with POAG or OHT: study design and population
The clinical study was conducted according to the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki, and written informed consent was obtained from each study participant prior to conducting any protocol-related procedures. The study was approved by the local independent ethics committees and health authorities.
The study was an adaptive, multicentre (three sites in USA, two in Czech Republic and one in Hungary), randomised, investigator-masked (during the randomised treatment phase), subject-masked, multiple-dose, placebo-controlled, parallel study to investigate efficacy, safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of RO5093151 for up to 28 days in subjects with POAG or OHT. It was conducted from December 2011 to November 2012 (NCT01493271).
Patients who had given written informed consent were screened within 8 weeks prior to the start of the lead-in phase. A wash-out phase for up to 6 weeks was conducted during the screening phase for patients on previous treatment (corticosteroids, systemic or ocular medication known to affect IOP, glaucoma medications). Screening assessments included medical history (general and ophthalmological), physical examination, height and weight, 12-lead ECG, vital signs including blood pressure and body temperature, drugs of abuse and alcohol test, blood and urine clinical laboratory safety tests (haematology, coagulation, chemistry, urinalysis and serology), pregnancy test as appropriate and a thorough ophthalmological examination (biomicroscopy and best corrected Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) visual acuity, pachymetry, gonioscopy, visual field and fundus examination under dilatation).
Patients started with a subject-masked 7-day run-in period (from days −7 to −1) with twice daily dosing of placebo, followed by a 7-day treatment phase with twice daily dosing of RO5093151 200 mg or placebo randomised at a ratio of 4:1 (days 1–7, at 08:00 and 18:00) using an interactive voice recording system for treatment group allocation. During the treatment phase, investigators and patients were masked, while selected members of the study team from the sponsor were unmasked to allow interim analysis.
A dose of 200 mg twice daily was chosen as it was the highest daily dose tested in previously conducted phase 1/2 studies following multiple dose administrations12 13 and revealed to be safe and well tolerated with a treatment duration of at least 4 weeks. Already a 5 mg twice daily regimen was shown to inhibit the conversion of cortisone to cortisol (see urinary cortisone/cortisol metabolite assessment below) to a similar extent observed at higher doses (data not shown). High inhibition was also shown at a dose of 50 mg for hepatic and adipose 11βHSD1 (data not shown).
Time-matched IOP assessments (Goldmann Applanation Tonometry) were performed on days −7, –1, 1 and 7 at 1-hour predose, at time of dosing (0 hour) and at 1, 2, 4, 8 and 12 hours postdose, referring to the first daily dose administered at 08:00. Additional 1-hour postdose IOP assessments were performed on days 4 (on treatment), 14 and 21 (follow-up days). Spot urine samples for assessment of the urinary ratio of 5α-tetrahydrocortisol (5αTHF)+5β-tetrahydrocortisol (THF) over tetrahydrocortisone (THE) (THF/THE) were collected on days of IOP assessment (except for day −7) also in a time-matched manner. Serum cortisol and ACTH were collected on days −1, 7 and 21 (data not shown). Sparse pharmacokinetic samples were taken on day 7; plasma concentrations of RO5093151 were assessed using a validated LC-MS/MS assay (limit of quantification (LOQ)=0.5 ng/mL).
Inclusion criteria included male and female patients of at least 21 years of age, inclusive, diagnosed with OHT or POAG in at least one eye, a cup-to-disk ratio ≤0.8, best corrected visual acuity of 6/30 or better, central cornea thickness of 420–620 µm and able to participate and willing to give informed consent. Patients with intraocular hypertension were required to have an IOP ≥22 mm Hg at 08:00 (±1 hour) and ≥18 mm Hg between 15:00 and 18:00 in at least one eye and ≤32 mm Hg at all time-points in both eyes at screening and on day −7. Subject with diagnosed glaucoma had to have an IOP ≥18 mm Hg at screening and IOP ≥22 mm Hg on day −7, at 8:00 (±1 hour) and at the afternoon measurement, in at least one eye. The worse eye was defined as the eye with the higher IOP at baseline (day −1, time matching 1-hour postdose).
Patients with the following criteria were excluded: presence of extreme narrow angle with complete or partial closure, progressive retinal or optic nerve disease from any cause other than glaucoma, history or signs of penetrating ocular trauma, uncontrolled hypertension despite treatment, clinically significant abnormalities in laboratory test results, positive test results on hepatitis B, hepatitis C or HIV 1 and 2, kidney disease or dysfunction.
Statistical analysis
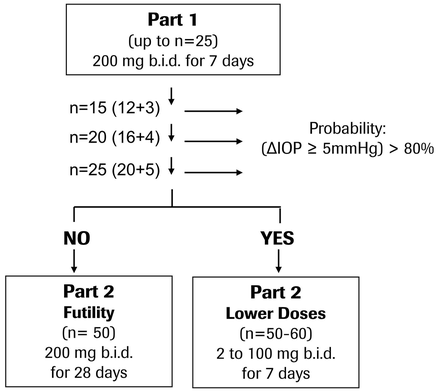
The primary endpoint of the study was the change from baseline for IOP measured on day 7 at 1-hour postdose and baseline being the time-matched IOP on day −1. The following Bayesian decision criterion was applied to the primary endpoint when a predefined number of patients had completed day 7 assessments:
Probability (ΔIOP ≥5 mm Hg)>80% based on the posterior distribution of the mean ΔIOP.
The Bayesian analysis was performed three times (figure 1), after the following number of evaluable subjects on RO5093151 was achieved: n=12 (15 including placebo), n=16 (20 including placebo), n=20 (25 including placebo). If the decision criterion had not been reached with 25 evaluable patients, additional 35 evaluable patients would have been enrolled and treatment duration would have been prolonged to a total of 28 days (part 2a) (figure 1). If the decision criterion had been reached, it was planned to include the investigation of lower doses and dose response of RO5093151 (part 2b). As the clinical study was terminated after completion of part 1, no further description of part 2 is provided.
Flowchart of clinical study design. The study was terminated after completion of part 1.
Results
Exploratory study to assess ocular exposure of RO5093151 in the rabbit
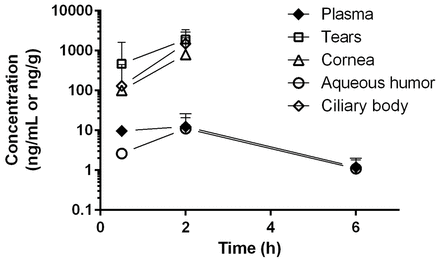
Following a single oral dose of 30 mg/kg RO5093151 to the rabbit, low plasma concentrations were observed, with mean quantifiable levels up to 6-hour postdose. In aqueous humour, RO5093151 levels were also quantifiable up to 6 hours, whereas the other eye tissues exhibited quantifiable RO5093151 exposures only up to 3-hour postdose (figure 2). Despite the low plasma exposure, a high distribution into the investigated ocular tissues was observed, with tissue/plasma ratios of 209, 133, 20 and 0.6 for tears, ciliary body, cornea and aqueous humour, respectively, at 2-hour postdose where highest concentrations were achieved.
Tissue concentrations of RO5093151 following single oral administration of 30 mg/kg RO5093151 to rabbits. Each data point reflects the mean of individual concentration of ocular tissue (from both eyes) and plasma of three animals. Results of the ocular tissues from one eye at 2-hour postdose were excluded from the analysis due to implausible high concentrations as compared with the results from the other eyes at the same time-point. Concentrations below the detection limit were set to 0 for mean calculation.
Clinical efficacy, safety and tolerability of RO5093151 in patients with POAG or OHT
A total of 35 patients were enrolled into the study; of these, 34 patients entered the placebo lead-in phase and 32 patients were randomised to either 200 mg twice daily RO5093151 (n=26) or matching placebo (n=6). All subjects who were randomised and received treatment were included in the intention-to-treat (ITT) population for the safety analysis. Six subjects were excluded from the per-protocol (PP) analysis; two each were excluded due to non-adherent drug intake, inclusion criteria violation and closure of a site. The ‘better eye’ of one subject was excluded from the PP analysis due to non-eligibility of this eye (previous trabeculectomy).
Most of the patients were female (15/25 subjects) with a mean age of approximately 60 years. The majority of patients had POAG (approx. 70%). All subjects who participated in the study reported angular widths of >20° (wide) and were classified to Shaffer Scale scores 2–4 and reported central cornea pachymetry measurements of 454–610 µm in each qualifying eye (inclusion criterion 420–620 µm) at baseline. The mean (SD) baseline IOP on day −1 at the nominal 09:00 time-point was 24.5 (3.1) and 23.4 (1.6) mm Hg for the RO5093151 and placebo group, respectively.
Safety and tolerability
RO5093151 was well tolerated in all subjects. Three subjects on active treatment reported in total four adverse events (diverticulum, osteoporosis, urinary tract infection and protein present in urine), which were all judged by the investigators to be not related to drug treatment. The reported adverse events were mild in intensity and resolved with no sequelae. No subject on placebo, either during the placebo run-in phase or during the randomised treatment phase, reported any adverse event. No clinically significant changes in vital signs, clinical laboratory values, general safety ophthalmological assessments and ECG readings were noted.
Pharmacodynamics
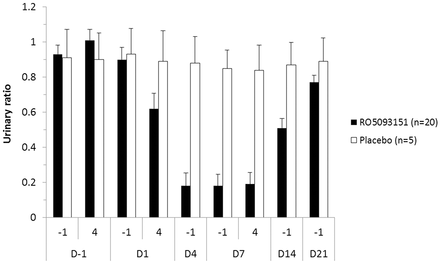
A high and sustained inhibition of 11βHSD1 was shown in the RO5093151-treated group by the decrease of urinary THF/THE from between 0.9 to 1 at baseline to 0.18 on days 4–7 (figure 3), with no apparent changes in the placebo-treated group. After cessation of active treatment, the THF/THE ratio gradually returned to values close to baseline within 14 days, with the ratio in the active group still slightly below the baseline value.
Mean (+SEM) urinary (5αTHF+5βTHF)/THE ratio as measure of 11βHSD1 inhibition (PP population). Randomised treatment (RO5093151/placebo) started on day 1 and lasted until day 7. PP, per-protocol; THE, tetrahydrocortisone; THF, tetrahydrocortisol.
Pharmacokinetics
The mean (SD) RO5093151 trough concentrations were at 124±127 ng/mL (n=20, PP analysis), ranging from 20 to 440 ng/mL, except for one patient with undetectable concentrations.
Intraocular pressure
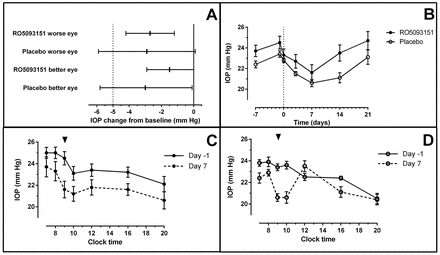
The mean baseline IOP values (day −1) in the active treatment group were slightly higher than in the placebo group. Mean IOP was highest in the morning, with a gradual decrease during the course of the day and a sometimes apparent additional peak around lunchtime (figure 4C,D). There was a gradual trend for an overall decrease in IOP with time for both the placebo and active treatment groups, while a return to baseline values was observed after treatment cessation (figure 4B).
Effect of RO5093151 and placebo on IOP. (A) Adjusted least square mean change from baseline and 95% CI in IOP from ANCOVA model at 1-hour postdose on day 7 versus time-matched 1-hour postdose on day −1. (B) Mean (±SEM) 1-hour postdose IOP profile for RO5093151 and placebo-treated patients over the study period. (C) Mean (±SEM) IOP time profile for RO5093151-treated patients (worse eye) for days −1 and 7. (D) Mean (±SEM) IOP time profile for placebo-treated patients (worse eye) for days −1 and 7. Arrow indicates time-point of primary endpoint (1-hour postdose); clock time shown for C and D. ANCOVA, analysis of covariance; IOP, intraocular pressure.
In the ‘worse eye’, the adjusted least square mean change from baseline in the PP population was −2.7 mm Hg (95% CI −4.2 to –1.2) and −2.9 (95% CI −5.9 to 0.1) in the RO5093151 and placebo group, respectively, with a mean difference between RO5093151 and placebo of 0.2 mm Hg (95% CI −3.1 to 3.6), in favour of placebo. In the ‘better eye’, displaying better IOP values at baseline compared with the selected worse eye, the adjusted least square mean change from baseline was −1.5 (95% CI −2.9 to 0.0) and −3.0 (95% CI −5.8 to −0.1) in the RO5093151 and placebo group, respectively, with a mean difference between RO5093151 and placebo of 1.5 (95% CI −1.7 to 4.7), in favour of placebo (figure 4A).
While there was a statistically significant IOP reduction in the change from baseline for the ‘worse eye’ in the active treatment group and for the ‘better eye’ in both active and placebo treatment groups, the ANCOVA model adjusting for baseline levels did not show statistically significant difference in change of IOP between the active treatment group and placebo for both the ‘worse eye’ and the ‘better eye’.
The Bayesian decision criterion applied to the primary endpoint highlighted that the probability to reach the target reduction of at least 5 mm Hg was very low even at the final analysis with 20 subjects on active treatment (p=0.003).
Discussion
Published results from oral administration of the non-selective 11βHSD1 and 11βHSD2 inhibitor carbenoxolone8 and the cortisol biosynthesis inhibitor metyrapone14 were promising in supporting the rationale that a selective and potent inhibition of 11βHSD1 may achieve clinically relevant reductions in IOP following oral administration (table 1).
Key trial characteristics and IOP and pharmacological effects of orally administered drugs in clinical trials to reduce cortisol levels
The current study was designed as an exploratory proof of concept and included only a limited number of patients on placebo. Even when discarding the change from baseline for placebo due to the low number of patients on placebo included, the IOP effect of 2.7 mm Hg in the active treatment group had a very low probability (p<0.005) to achieve an IOP reduction of 5 mm Hg at 1-hour postdose but also at any time-point assessed. This target reduction was chosen for the decision criterion as it reflects a clinically relevant IOP reduction of approximately 20%, as achieved by ocular antihypertensive medications already on the market. The timing of the primary endpoint was chosen to be in the morning, as cortisol levels are known to be highest in the morning. Maximum concentration of RO5093151 (data not shown) is expected quickly after dosing, at approximately 1-hour postdose. IOP decreased over time from day 1–7 for both the active treatment and the placebo groups (figure 4).
The specific adaptive design of the study would have enabled to adapt the study conduct based on the sequential interim analyses using a Bayesian decision criterion. If the treatment duration of 7 days had not been achieving the target IOP reduction, the study protocol would have planned a prolongation of the treatment duration from 7 to 28 days. This was based on the bipartite rationale of the mode of action of RO5093151 on reduction of aqueous humour production and reduced outflow of aqueous humour.10 However, if the analysis had shown the anticipated IOP reduction, lower doses would have been tested to assess the dose-response of 11βHSD1 inhibition on IOP reduction. However, the study was discontinued due to portfolio reprioritisation prior to extending the treatment duration to 28 days.
The results of the presented study are in line with a similar type of study investigating the impact of another selective and potent oral 11βHSD1 inhibitor AZD4017 on IOP (table 1).15 16 However, AZD4017 was administered for a duration of 4 weeks, suggesting that a longer treatment duration in the present study may also not have provided a larger effect on IOP.
A weakness of the present study and clinical studies reported so far is the lack of demonstrating adequate ocular exposures of the investigational drugs following oral administration. Sampling of aqueous humour is an established methodology in clinical research, not so much for glaucoma specialists though, and could have provided highly valuable data on ocular drug exposure and ocular cortisol levels under treatment.
Our preclinical data suggest high drug exposure in ocular tissues following oral administration (figure 2). Aqueous humour concentrations were close to the unbound plasma concentrations, and a high ciliary body concentration indicates that RO5093151 reaches its target in the rabbit eye. In the clinical study, an oral dose of 200 mg RO5093151 twice daily was used in order to aim for a maximised ocular exposure. This dose is 40-fold above a dose level achieving a similar systemic THF/THE ratio and is still not interfering with 11βHSD212. Plasma RO5093151 trough concentrations measured on day 7 demonstrated unbound concentrations 60-fold to 1300-fold above the in vitro IC50 of 0.19 ng/mL, characterised for RO5093151 using H4IIE cells stably transfected with a cDNA encoding full-length human 11βHSD1 (data not shown). Assuming aqueous humour and ciliary body fluid concentrations being close to the unbound plasma concentrations in humans, as suggested in rabbits, a high inhibition of ocular 11βHSD1 by RO5093151 should therefore have been achieved in our study. However, it is unclear whether the blood–aqueous humour barrier limits the entry of the investigated drugs to the aqueous humour and subsequently to the ocular target tissue in humans. Furthermore, a theoretical compensatory response diminishing local cortisol reductions in ocular tissues cannot be ruled out.
In conclusion, there was no clinically meaningful IOP reduction by a 7-day oral treatment with RO5093151. Results of this study are in line with previously reported clinical data of compounds administered orally in the same class of 11βHSD1 inhibitors. Oral administration of RO5093151 200 mg twice daily for 7 days was safe and well tolerated. Whether topical administration or a longer exposure of RO5093151 would have achieved a clinically relevant result is currently not elucidated.
References
Footnotes
Acknowledgements The authors would like to thank Dr Svetlana Spassova, Senior Medical Director at PPD, Sofia, Bulgaria, for scientific advice regarding the definition of ocular inclusion and exclusion criteria and the principal investigators Mária Ferencz (Fövárosi Önkormányzat Szent Imre Kórház, OSZMSZ Szemészeti Profil, Budapest, Hungary), Jara Hornova (Fakultni Nemocnice Kralovske Vinohrady, Oftalmologicka Klinika, Praha, Czech Republic) and Jana Kadlecová (Oční klinika FN, Hradec Králové, Czech Republic) for participating to the trial.
Contributors DS, PJ, SF-R and WCS designed the clinical study.
DH designed, analysed and provided contribution to the preclinical study.
CS, AP, SF-R were involved in the design and analysis of the data.
MET and HD were responsible for data acquisition and research execution. A
ll authors were involved in revising and final approval of the manuscript.
Competing interests DS, CS, AP, SF-R, DH and PJ were employees of F. Hoffmann La Roche Ltd. The study was funded by Roche Pharmaceutical Research and Early Development.
Patient consent Patient.
Ethics approval Health authority approval in the USA, Bulgaria, Hungary and Czech Republic, corresponding ethics approval by Quorum Review IRB, Ethics Committee for Multi-centre Trials, Egeszsegugyi Tudomanyos Tanacs, Eticka komise Fakultni nemocnice, respectively.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.